Plastic pollution has become one of the biggest environmental threats of our time. With millions of tons of plastic entering our oceans, landfills, and ecosystems each year, scientists are racing to find sustainable solutions. Among the most promising discoveries is plastic eating bacteria, a groundbreaking biological tool that could transform how we manage plastic waste forever.
In this blog, we’ll explore what plastic eating bacteria are, how they work, why they matter, and how they may shape the future of waste management.
Understanding Plastic Pollution and Its Global Impact
Plastic pollution affects every corner of the planet — from urban cities to the deepest parts of the ocean. With over 300 million tons of plastic produced annually, only a small percentage is ever recycled. This problem continues to grow, threatening wildlife, contaminating food chains, and reducing soil and water quality.
Why Traditional Recycling Isn’t Enough
Traditional recycling is expensive, inefficient, and limited. Many types of plastic cannot be recycled at all, and even recyclable plastics often end up in landfills due to sorting issues.
The Scale of Plastic Waste Today
- Over 8 million tons of plastic enter the oceans every year
- Microplastics are found in human blood, rainwater, and food
- Plastic takes hundreds of years to break down
Clearly, a new solution is urgently needed — and that’s where plastic eating bacteria come in.
What Are Plastic Eating Bacteria?
Plastic eating bacteria are microorganisms capable of breaking down and consuming plastic as a food source. These microbes use special enzymes to degrade plastic polymers into simpler, harmless compounds.
Discovery of Ideonella sakaiensis
In 2016, researchers in Japan discovered Ideonella sakaiensis, a bacterium capable of breaking down PET (polyethylene terephthalate), a common plastic used in bottles and packaging. This moment changed the scientific community’s understanding of plastic biodegradation forever.
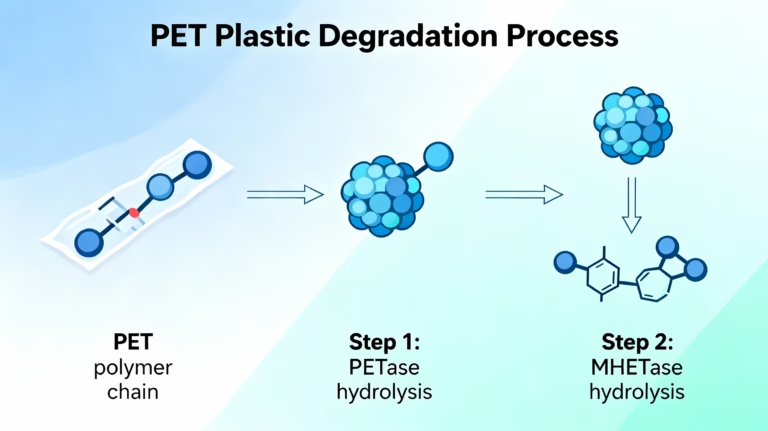
How Plastic Degradation Works at a Biological Level
These bacteria produce enzymes that soften and break apart plastic molecules.
PETase and MHETase Enzymes
- PETase: breaks down PET into smaller molecules
- MHETase: further digests the molecules into environmentally friendly components
This biological process is natural, clean, and renewable.
How Scientists Are Enhancing Plastic Eating Bacteria
To make bacteria more effective, scientists are improving their speed and efficiency.
Genetic Modification for Faster Breakdown
Using gene editing tools like CRISPR, researchers are enhancing bacterial enzymes to work faster and at scale.
Laboratory Experiments and Real-World Trials
Recent experiments show bacteria can break down plastics in just days, not years, under controlled environments.
Benefits of Using Plastic Eating Bacteria
This biological solution could revolutionize how we approach waste.
Eco-Friendly Waste Management
Unlike burning or melting plastic, bacterial degradation produces no toxic emissions.
Reduction of Microplastic Pollution
Plastic eating bacteria break plastic down completely, preventing microplastic formation.
Low-Cost Waste Processing
Unlike industrial recycling, bacteria require minimal energy and infrastructure.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their promise, plastic eating bacteria face several challenges.
Slow Breakdown Rate in Natural Environments
They work best in controlled environments, not in oceans or open landfills.
Safety Concerns and Ecosystem Risks
Introducing modified bacteria into the wild may have unknown consequences.
Future Applications of Plastic Eating Bacteria
Scientists envision many powerful uses.
Industrial Waste Facilities
Factories could integrate biochambers filled with bacteria to digest plastic waste.
Ocean Cleanup Initiatives
Advanced bacterial systems may be installed in floating cleanup devices.
Consumer-Level Biorecycling Products
One day, households may use microbial kits to recycle plastic at home.
Plastic Eating Bacteria vs. Traditional Recycling
| Feature | Plastic Eating Bacteria | Traditional Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | Very Low | High |
| Emissions | None | Significant |
| Microplastic Risk | Minimal | High |
| Cost | Low | Medium–High |
| Plastic Types Supported | Expanding | Limited |
How Countries Are Using Biological Recycling
Japan’s Biotech Innovations
As the discovery place of Ideonella sakaiensis, Japan leads in bacterial recycling research.
Europe’s Zero-Plastic Initiatives
European countries are integrating biotechnologies into climate action programs.
FAQs About Plastic Eating Bacteria
1. Are plastic eating bacteria safe for the environment?
Yes — when used in controlled environments, they pose minimal risk.
2. Can these bacteria clean the ocean?
Not yet, but future engineered strains may support ocean cleanup.
3. How fast do plastic eating bacteria work?
Some enhanced strains can break down plastic within days.
4. Is this technology available for public use?
Not currently, but biotech companies are developing industrial solutions.
5. Do they work on all plastics?
They currently work best on PET, but new strains are being developed.
6. Will plastic eating bacteria replace recycling?
They will likely complement recycling, not replace it.
🔗 See Also: The 10-3-2-1-0 Formula — a powerful routine to boost focus and sleep quality.
Conclusion
Plastic eating bacteria represent one of the most exciting breakthroughs in environmental science. With continued research, innovation, and responsible use, these remarkable organisms may become a primary tool in solving the global plastic crisis.
For further reading, explore environmental science resources like National Geographic.